The “20 ppi” ceramic foam filter has a very significant rectification effect, which can effectively solve the casting surface cracks. The ceramic foam filter effectively removes most of the inclusions in the melt, so that the deviation of the tensile strength, yield strength and elongation of the workpiece tends to be reduced, and avoids the sharp decrease of the mechanical properties caused by individual coarse inclusions. However, the “20 ppi” ceramic foam filter cannot filter out relatively small inclusions, so it cannot improve the overall level of tensile strength and yield strength. However, the filtration of individual coarse inclusions is beneficial to the improvement of the mechanical properties of the material.
The wheel structure of aluminum alloy wheels largely determines the difficulty of low-pressure casting. The reason for the cracks on the casting surface is that during the filling process of the casting, the turbulent flow of the molten metal forms secondary oxidation and entrapment, resulting in cracks on the casting surface and internal pores.
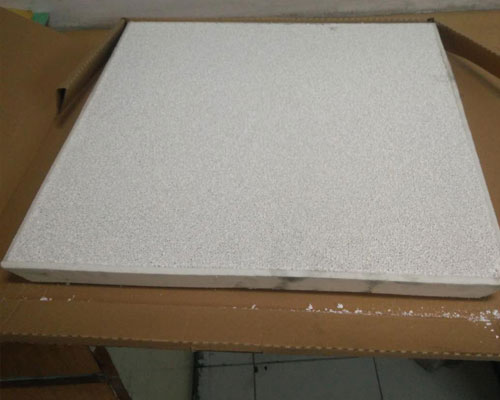
In order to avoid secondary oxidation and entrapment caused by the turbulent flow of molten metal, reduce the casting surface cracks and internal pores caused by this. After testing many different types, different models, and different specifications of filters, the “20ppi” ceramic foam filter produced by AdTech was finally selected.
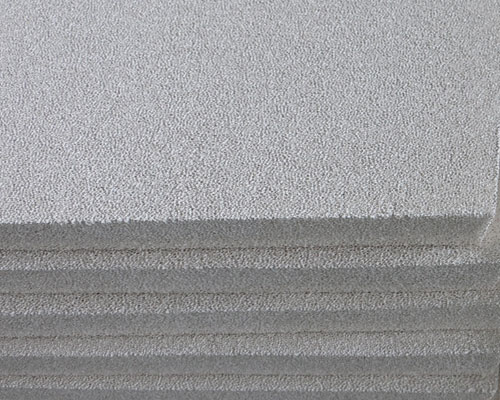

20 ppi is a model, which represents a foam ceramic filter plate product with a pore uniformity of 17 to 23 holes in any length of 25.4 mm. The “20ppi” ceramic foam filter is usually more effective in blocking inclusions with a particle size of 50 μm or more. With the passage of a certain amount of metal melt, a filter cake will form on the surface of the filter inlet, and thereafter the flow rate of the melt through the filter will be significantly reduced. On the one hand, due to the decrease in the inner diameter of the inlet, the probability of interception of smaller particle size inclusions increases, and the removal efficiency of small particle size inclusions increases; on the other hand, due to the reduction of the cross-sectional area of the molten metal flow channel, the molten metal Replenishment is blocked, and casting defects such as delayed feeding and shrinkage are likely to occur.
After using the ceramic foam filter, the rectifying effect of the ceramic foam filter can be fully demonstrated. The trickle of molten metal flowing through the ceramic foam filter merges into the mainstream of laminar flow. The laminar flow state of molten metal fills smoothly, avoiding secondary oxidation and entrapment of molten metal, and effectively solving the cracks on the casting surface.