In the process of aluminum melting and casting, bubbles, oxide film and non-metallic inclusions destroy the continuity of metal materials, reduce the effective bearing section of castings, and cause stress concentration, which reduces the mechanical properties and processing properties of castings. In order to avoid these hazards, in addition to cleaning the furnace charge, it is also necessary to purify the aluminum melt, which can be divided into the following three categories according to the different aluminum melt purification mechanisms and forms.
Aluminum Melt Purification Mechanisms
(1) Adsorption purification: in the smelting process, chlorine, nitrogen or inert gas is passed into the molten aluminum, or some chlorine salts (such as ZnC, MnCl, CCl4, etc.) that can react with molten aluminum to form bubbles are added, which is called bubble flotation, or KCl and NaCl are used to make flux, and the gas and inclusion in the alloy can be removed by the adsorption of refining agent
(2) Physical purification: with the help of physical processes, the aluminum melt is purified, such as ultrasonic treatment, DC treatment and vacuum treatment.
(3) Filtration purification: the liquid metal flows through a certain medium, and the inclusions are caught, thus purifying the metal.
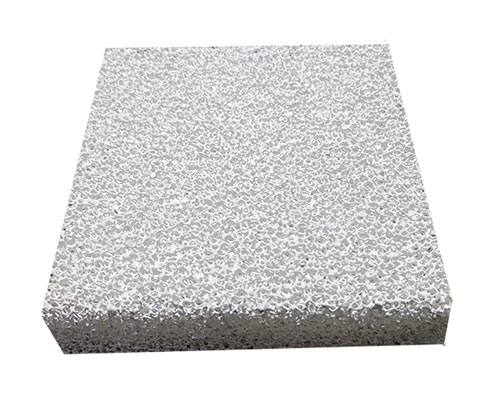

As early as 1978, the new filter developed by the United States and a ceramic foam filter is a very successful filtering medium. Its appearance provides a kind of high-efficiency filter for the production of cast aluminum parts.
Alumina ceramic foam filters are mainly used for filtration of molten aluminum and alloy in foundries. The filter has excellent resistance to molten aluminum corrosion and corrosion, can effectively remove inclusions, reduce residual gas and provide laminar flow, and then the filtered metal is significantly cleaner. Cleaner metals result in higher quality castings, fewer rejects and fewer inclusion defects, all of which contribute to higher profits.