Ceramic Foam Filter Filtration principle is the same as that of ceramic tube filtration. It is a deep filtration mechanism, which has a higher porosity than the ceramic tube (80%-90%). Therefore, it has great capacity for flow and is suitable for filtration and purification in continuous casting and continuous rolling production. It is the most effective method to remove inclusions in molten aluminum by using foam ceramic filter plate. In recent years, some new technologies, such as vacuum dynamic treatment, ultrasonic continuous degassing purification and corundum ceramic filter, have been studied at home and abroad, which have achieved good results. However, these processes are more complex and costly, so it is difficult to popularize them in the industry. The metal filter screen and fiber cloth filter used by low-end customers can only remove large inclusions in aluminum alloy melt, but cannot remove inclusions below micron level, and metal filter screen will pollute aluminum alloy. The foam ceramic filter plate can filter out small inclusions, and significantly improve the mechanical properties and appearance quality of the products.
The main advantage of the ceramic foam filter filtration system is that the slag inclusion generated in the process of injection outside the furnace can be effectively eliminated through the filter plate to remove the micron size small inclusions in the liquid aluminum which can not be done by the conventional process. At the same time, due to the small inclusions filtered out by the filter plate, the effective nucleation number in the liquid aluminum is reduced, so that the aluminum liquid nucleates and grows under a large supercooling condition, and the solidification time is shortened. The microstructure is refined and the hydrogen content in molten aluminum is reduced. Hydrogen atoms can be adsorbed on some oxidation inclusions, and the oxidation inclusions can become the core of bubble growth, so the gas on the inclusions can be removed at the same time; the harmful elements (sodium and potassium) in liquid aluminum can be removed by adsorption; therefore, according to different customer requirements or site environmental conditions, the selection of suitable filter plate to ensure product quality can effectively control slag inclusion.
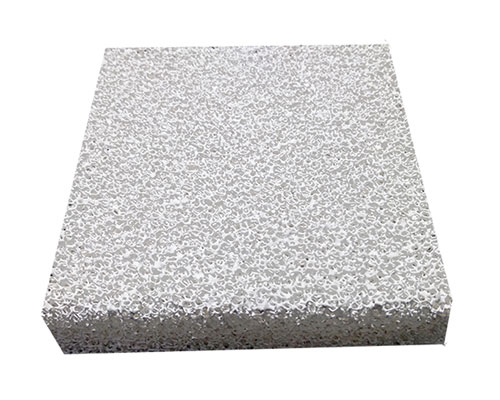

In addition to the ceramic foam filter, the ceramic plate is mainly connected with the multi-layer filter plate. During filtration, inclusions in the molten aluminum flow along the zigzag channels and pores, and are directly intercepted, adsorbed, and deposited when contacting with the foam like framework of the filter plate. When the melt flows in the pores, the channel of the filter plate is bent, and the melt flowing through the channel changes the direction of movement, and the inclusions are firmly attached to the wall of the hole against the hole anvil.
The foam ceramic filter is installed in the CFF filter box between the furnace mouth and the splitter plate. The closer the filter box is to the splitter plate, the better. The reason is that it can shorten the flow distance of liquid aluminum after filtration and reduce or avoid the reoccurrence of oxide. The aluminum liquid flows out of the furnace mouth, passes through the filter box, and then flows into the splitter plate through the launder. When the filtration device starts, the drop before and after the melt filtration is about 30mm. With the extension of the filtration time, the inclusions on the surface and hole wall of the filter plate increase, the filtration flow rate decreases, and the head drop increases. At the end of the casting, the drop increases to 50-100 mm. The selection of filter plate first depends on the filtering accuracy. Generally, the pore size of 10 holes/cm can meet the requirements of aluminum liquid purification. If the aluminum liquid is particularly dirty, the large aperture aluminum plate with 6 holes/cm is used for pre-filtration, which can prevent the micro-hole filter from blocking prematurely. Secondly, the area of ceramic foam filter is determined according to casting speed and metal flow rate per unit time.