The ceramic foam filter for foundry is installed in the filter box between the furnace and the distributing launder. The filter box is made of refractory material. It can undergo multiple chilling and heating without cracking, and has the advantages of high strength and good insulation performance.
The closer the filter box is to the splitter plate, the better, because this can shorten the flow distance of the aluminum liquid after filtration, and reduce or avoid the re-generation of oxides. The molten aluminum flows out of the furnace mouth, passes through the filter box, and then flows into the splitter plate through the launder. When the filter device is started, the drop before and after the melt filtration is about 50mm, but with the extension of the filtering time, the inclusions on the surface of the filter plate and the hole wall increase, and the drop of the filter flow rate increases. At the end of the casting, the drop increases to 60- -120mm.
The selection of the filter plate must be based on the flow of molten aluminum. Secondly, the high content of inclusions in the body and the total throughput of the melt should be considered. When designing the filter device, according to the specifications of the selected filter plate, and considering the drop of the furnace mouth and the splitter plate, it must be ensured that the filter plate is immersed in the molten aluminum during the melt casting. In addition, it must be considered that the installation and disassembly are safe and convenient, and the aluminum liquid in the filter box can be completely drained after the melt is cast.
Practice has proved that the ceramic foam filter for foundry is an effective tool for removing oxidized inclusions in the flame. General fiber filtration can only remove large inclusions, while the foam ceramic filter plate can simultaneously filter large inclusions and small inclusions.
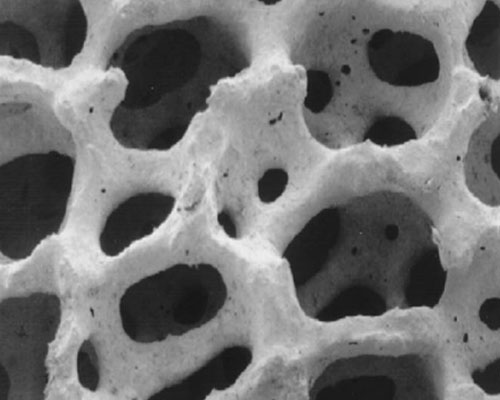
The ceramic foam filter for foundry has a multi-layer network and multi-dimensional through holes, and the holes communicate with each other. During filtration, liquid aluminum carries inclusions and flows along tortuous channels and pores. When it comes in contact with the foamed framework of the filter plate, it is directly intercepted, adsorbed, deposited and so on. When the body flows in the hole, the filter plate channel is curved, the melt flowing through the channel changes the flow direction, and the inclusions collide with the hole wall and firmly adhere to the hole wall.
The filtering effect of the ceramic foam filter plate is mainly ensured by the size and porosity. The larger the hole of the filter plate, the worse the slag removal effect. For aluminum castings with strict requirements, a filter plate with small holes should be selected. The foam filter plate is currently an effective tool for removing oxidized inclusions in the melt.

