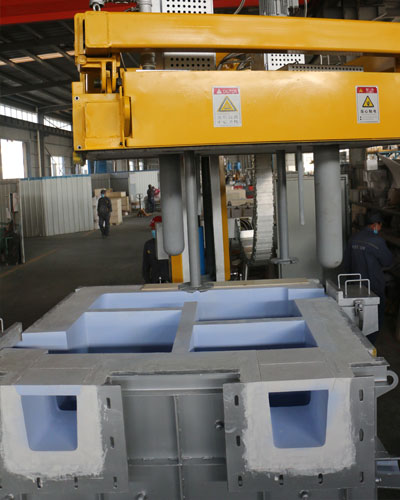
When the aluminum liquid enters the inlet of the degassing device, in order to prevent the air from entering the hydrogen removal device from the inlet, causing the increase of oxidized inclusions and affecting the hydrogen removal effect. Generally, the inlet position of the molten aluminum is designed to be lower than the liquid level of the molten aluminum in the launder, so that the inlet of the degassing device is immersed under the molten aluminum, and air cannot enter the refining tank, which improves the aluminum degassing effect.
The mouth of the degassing box is immersed in the aluminum liquid, and air cannot enter the degassing device, reducing the number of oxidized inclusions generated in the degassing box and improving the hydrogen removal effect.
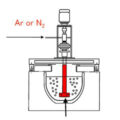
In order to reduce the air content in the refining tank, reduce the contact between molten aluminum and air, and reduce the oxidation degree of molten aluminum, while optimizing the inlet and outlet of the refining tank, the refining tank is filled with protective gas. The protective gas is N2 or Ar. Under the protection of inert gas, the aluminum liquid in the refining tank is not easy to oxidize, and it is not easy to absorb hydrogen, which improves the hydrogen removal effect.
In the process of hydrogen removal, hydrogen will be discharged from the refining tank after refining and draining from the molten aluminum at any time. Therefore, the protective gas must be maintained at a certain pressure, and the discharge valve of the refining tank will automatically be under a certain pressure. Open it to release the gas inside the refining tank. In this situation, the atmosphere in the refining box always maintains a certain positive pressure. While the hydrogen is released in time, it prevents air from penetrating into the refining box and avoids secondary hydrogen absorption by the aluminum liquid.

Due to the inert gas protection in the degassing unit, in an inert gas atmosphere, H2 cannot be burned without the presence of O2, but at the position of the gas discharge port, the gas is discharged from the hydrogen removal device, and the high temperature H2 contacts the O2 in the air. It burns immediately, so there is a flame at the position of the gas discharge port. This is due to the phenomenon that H encounters O2 in the air to produce combustion.
The graphite rotor is used to remove the hydrogen in the aluminum liquid through the adsorption of inert gas, which is the main process for online hydrogen removal. However, during the process of inert gas bubbles floating in the molten aluminum, the temperature of the molten aluminum is as high as 720°C. At the same time, the pressure of the molten aluminum on the bubbles gradually decreases during the floating of the bubbles, causing the volume of the bubbles to expand, and the bubbles will interact with each other. Due to the volume expansion, they are combined together, which reduces the total area of the bubbles in contact with the molten aluminum and reduces the efficiency of hydrogen removal.