Filtering with CFF is a supplement to metal treatment within the furnace, such as fluxing and degassing or inline filtration. Ceramic foam filters offer a simple, reliable, and cost-effective method to remove inclusions.
With the demand for high quality aluminium products increasing, filtering with CFF has proved an optimum method for improving metal quality. Technical advances in CFF, such as fine pore filters and improved filtration systems better suited to the stringent operating conditions of the casthouse have offered an efficient method of removing inclusions from liquid aluminium in a wide range of critical applications.
For ceramic foam, their good thermal resistance and high porosity characteristics led to use as filters in the purification of liquid metals, which are still the largest application today. Ceramic foam is also used for catalytic combustion, burner enhancers, soot filters for diesel engine exhausts, catalyst supports, and biomedical devices. It is widely accepted that based on their structural properties, CFFs can remove exogenous and indigenous inclusions in the melts, and moreover, have low flow resistance and high filtration efficiency.
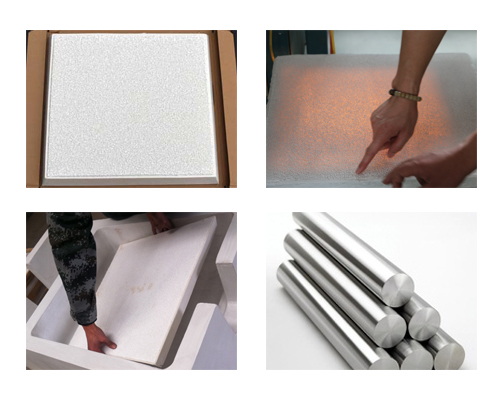
The ceramic foam filter and filter bowl for use in the removal of solid inclusions from liquid metal. The filters are integrated into filter boxes and applied to the casting process directly in front of the casting unit.
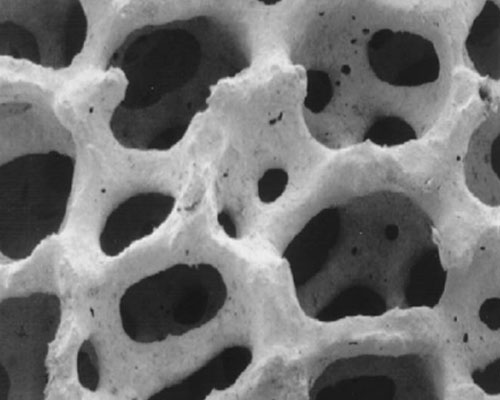
The chemical composition of the CFF is mainly alumina. The porosity of the filter is around 85 to 90%. The ceramic particle density is 3.48±0.02 g/cm3. Alumina ceramic foam filters have been widely used for filtering impurities out of molten aluminium in cast houses. With their excellent resistance to attack and corrosion from molten aluminum, they can effectively remove inclusions, reduce trapped gas and provide laminar flow, and then the filtered metal is significantly cleaner. Cleaner metal results in higher-quality castings, less scrap, and fewer inclusion defects, all of which contribute to bottom-line profit.

