Foam ceramic filters are mainly used to purify molten aluminum, and are used in the production of strips, foils and their products (such as can blanks, car finishing materials, PS printing plates, etc.). The foam ceramic filters can effectively remove various inclusions with a fineness of micrometers in the molten aluminum, so that the aluminum water becomes a smooth laminar flow.
The ceramic filter plate is surrounded by a sealing lining, which acts on the contact surface of the filter plate and the filter box to prevent the aluminum liquid from leaking through the contact surface. Our oxygen foam ceramic filter board uses three different specifications of sealing gaskets: fiber paper edge; fiber cotton edge; expanded cotton edge.
Product advantages of ceramic foam filter
- Adopting the principle of adsorption to filter, which can effectively remove large inclusions in molten aluminum and effectively adsorb small and small inclusions;
- No slag drop, effectively reducing pollution to molten aluminum;
- Good thermal shock resistance and improved corrosion resistance to molten metal;
- Automated assembly line production, three calibration procedures, accurate size, more in line with the filter box;
- The role of improving surface quality, improving product performance, and improving microstructure.
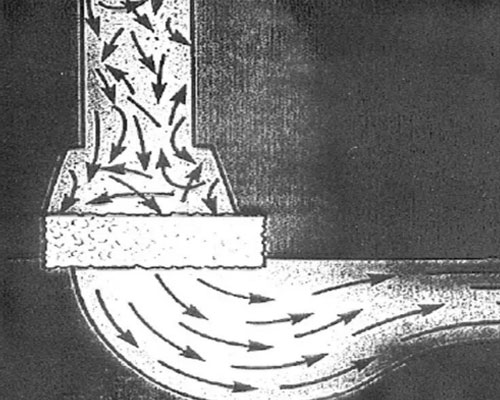
Foam Ceramic Filters for Molten Aluminum Filtration
The complex ceramic foam structure can effectively block slag mechanically. When molten metal passes through a ceramic foam filter with a complex structure. Through the mechanical separation of the filter medium, the inclusions larger than the pores on the surface of the filter are filtered out and precipitated at the inflow end of the liquid metal of the filter, becoming an integral part of the filter.
As the number of inclusions accumulated on the surface of the filter increases, a layer of “filter cake” is gradually formed, which makes the metal liquid flow channel further thinner, so the new filter medium surface can filter out finer inclusions.
At the same time, the inside of the medium also has a filtering effect. Among the many small holes that penetrate the ceramic body, some show tiny slits, and some have dead ends. These areas with different changes are possible locations for intercepting inclusions, and there is also a “filter cake” effect inside the filter.
When the molten metal flows through the ceramic body with complex structure, it is divided into many small streams, which increases the contact area between the inclusions in the molten metal and the filter medium. Because the surface of the filter is extremely small convex and concave surface, the size of the concave block It is about 1~10μm, and it has electrostatic adsorption and adhesion interception effects on inclusions.
When molten aluminum flows through the ceramic foam filter, it is divided into streams of many small units, and the liquid flow tends to move in laminar flow. When the molten metal is in a laminar flow state, since the density of the molten metal is much greater than the density of the inclusions, the inclusions have sufficient time to float up and remove, that is, the foam ceramic filter can assist the runner to stop the slag. After the filter is placed in the gating system, the resistance to the flow of the molten metal increases. The molten metal flowing in the runner easily forms a full motion and reduces the flow rate, which is beneficial for the inclusions to float and stay in the filter box.

