There are many and molten aluminum filtration methods for removing solid particulate impurities before introducing metal into the mold.
There are the following molten aluminum filtration methods:
Many known prior art flux and filtration systems use a filter medium that includes a bed of loose refractory particles, such as alumina balls, through which molten aluminum and flux gas flow counter currently. However, with the prior art granular filter media, it is not easy to control the size of the particles to be filtered, and the filter bed often suffers from channel problems, which leads to loss of filtration efficiency and frequent clogging. Of course, a clogged filter bed needs to be shut down to remove and replace the filter bed, or at least the casting operation needs to be interrupted to clean the filter bed on site.
However, when using a glass cloth filter, extreme care must be taken to prevent it from breaking, because high-temperature molten aluminum will have a harmful effect on the strength of the glass fiber. In many cases, existing filtration systems using glass cloth filters become ineffective due to the rapid accumulation of a large amount of particulate matter, resulting in clogging of the filter medium and the need to terminate the operation of replacing or renewing the filter medium.
Generally, especially when the filter is contaminated with filtered particulate matter, the downstream side of the glass cloth filter may be exposed to the air due to the position or direction of the filter or due to the flow rate of removing the filtered metal. This leads to the formation of alumina on the downstream side of the filter, and an undesirably large pressure difference on the filter, the pressure of which may rupture the pressure.
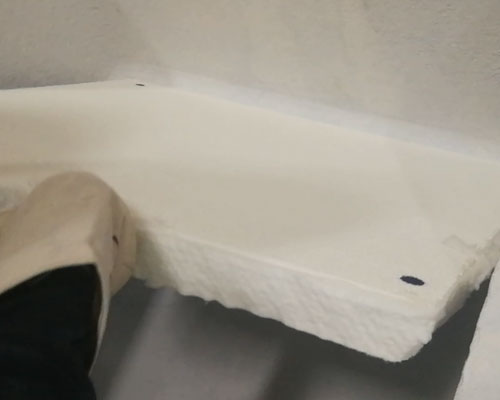

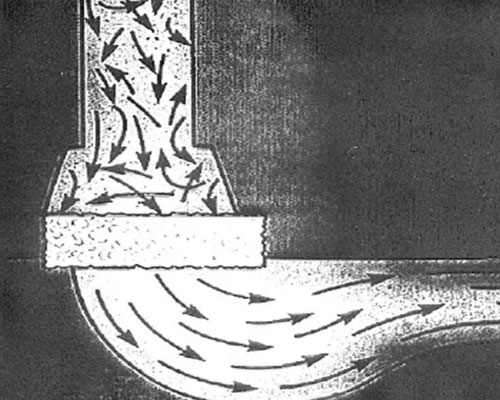
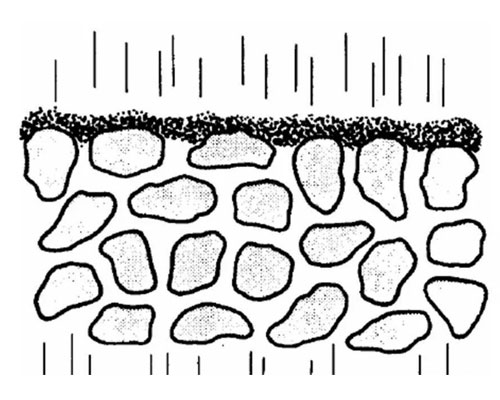
AdTech provides alumina ceramic foam filter plates, installed in the filter box, used for filtering aluminum alloy liquid impurities, and filtering molten aluminum before introducing it into the casting machine. It can meet the needs of producing high value-added, high-tech performance aviation, transportation and other aluminum alloy precision castings.
The ceramic foam filter plate uses a three-dimensional network structure and is connected to the pores of the organic foam as a carrier. It invades the thixotropic alumina slurry. The four-square-corrected center distance automatic extrusion technology is used to evenly coat the slurry on the carrier. The foam is on the body skeleton and cured at a high temperature of 1180°C.