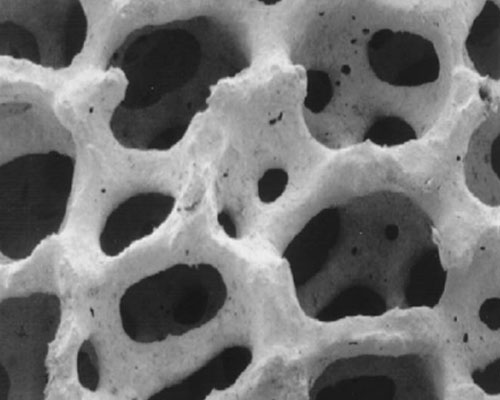
With the advancement of the preparation process, ceramics have acquired more novel forms, such as porous structures. Due to the large number of interconnected or closed pores in porous ceramics, it has the characteristics of low volume density, high specific surface area, and low thermal conductivity. In recent years, porous ceramics application has shined in environmental protection, smelting, chemical and other fields.
Porous Ceramics Application
The high specific surface area of porous ceramics gives it good adsorption capacity and activity. As a catalyst carrier, it can increase the effective contact area and improve the catalytic effect. At the same time, due to its excellent thermal shock resistance and corrosion resistance, it can be used in extremely harsh environments.
An excellent catalyst carrier must not only have stable chemical properties and be able to withstand the corrosion of acids, alkalis and other organic solvents, but also need to withstand high temperature changes during the production process without slagging; the most important thing is that the specific surface area is large enough. The specific gravity is as small as possible to reduce the weight. If the gas can form pulses as it passes, the catalytic effect will be better.
Filtration and Separation
The so-called filtration separation is the separation of solid particles suspended in liquid or gas, or two immiscible liquids.
The porous ceramic filter device has the characteristics of a large filtering area and high filtering efficiency. With its own high-temperature resistance, abrasion resistance, and corrosion resistance, in addition to conventional applications such as water treatment and gas filtration, it is used in some high temperature fields. It can also play a role, such as molten metal filtration.
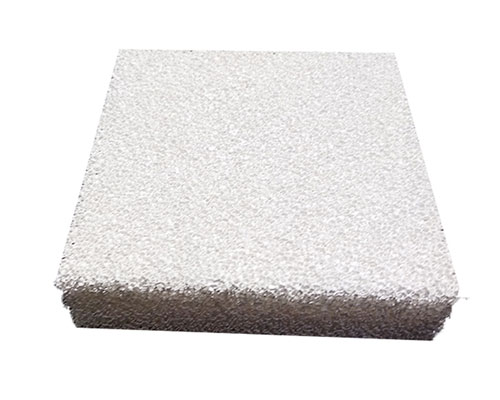

Nowadays, with the improvement of the quality requirements of aluminum products, the application of ceramic foam filter plates has also been promoted. The porosity of the ceramic filter plate is between 80% and 90%, which can effectively eradicate the micron-sized fine inclusions in the molten aluminum that are incapable of the conventional process. At the same time, because the fine inclusions are filtered out, the effective number of crystal nuclei in the molten aluminum is reduced. , So that the aluminum liquid nucleates and grows under relatively large supercooling conditions, the solidification time is shortened, and the structure is refined. In addition, through adsorption, the ceramic filter plate can also remove the harmful elements (Na, K) in the aluminum liquid. When aluminum alloy is filtered, the filter plate is heated and expanded instantly, so the filter plate is required to have a small thermal expansion coefficient to ensure that it does not crack when heated.